Cellular Respiration Formula Explained
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is c6h1206 6o2 6co2 6h2o energy atp.
Cellular respiration formula explained. This type of respiration is common in most of the. Cellular respiration formula explained. It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food.
C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 38ATP Glucose 6 Oxygen 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water ATP. During this activity the students work with a group to discuss the compounds and conditions that need to be present in order. Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
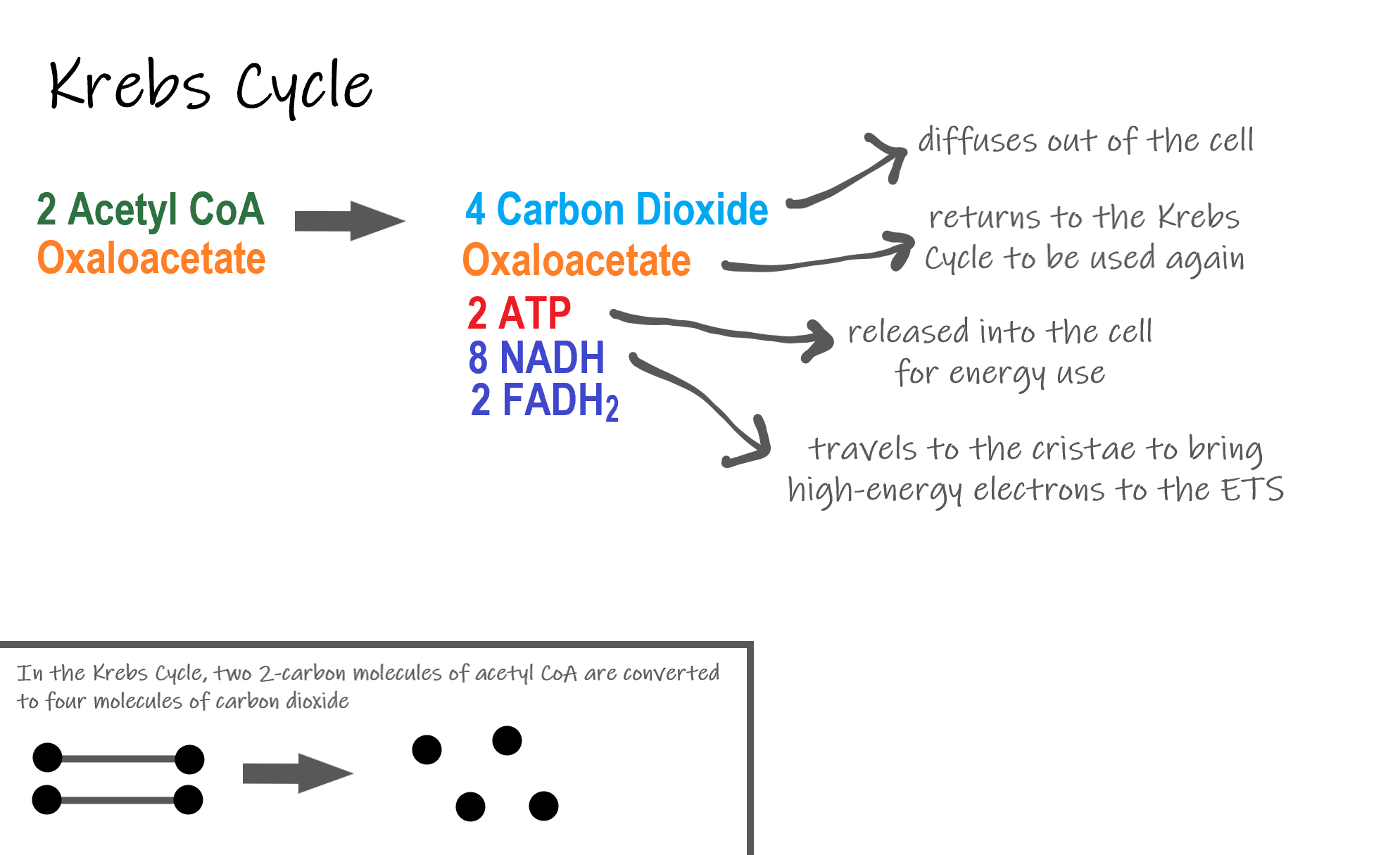
The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Cellular respiration can be summarized as glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water atp energy cellular respiration in plants. After reviewing the notes about cellular respiration and fermentation the students turn in the notes they have written either online or on paperThe students then take out their Chromebooks and enter the lab where we work on the fermentation demonstration activity.
Chemical structures of nad and nadh. Cellular respiration formula explained. This is the balanced equation that yields energy.
The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is. Glucose oxygen chemical energy carbon dioxide water Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create atp a chemical which the cell uses for energy. The process of cellular respiration involves many different steps reactions to break down glucose using oxygen to produce carbon dioxide water and energy in the form of ATP.
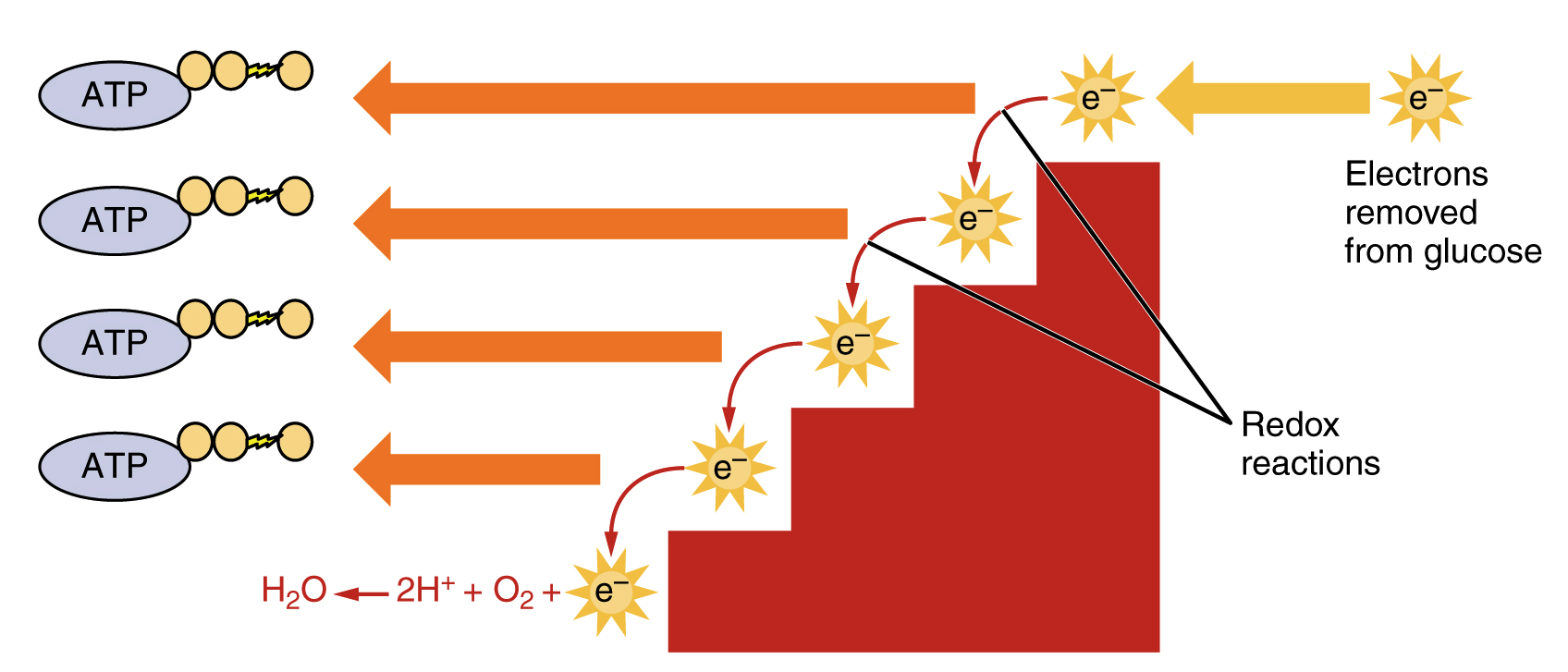
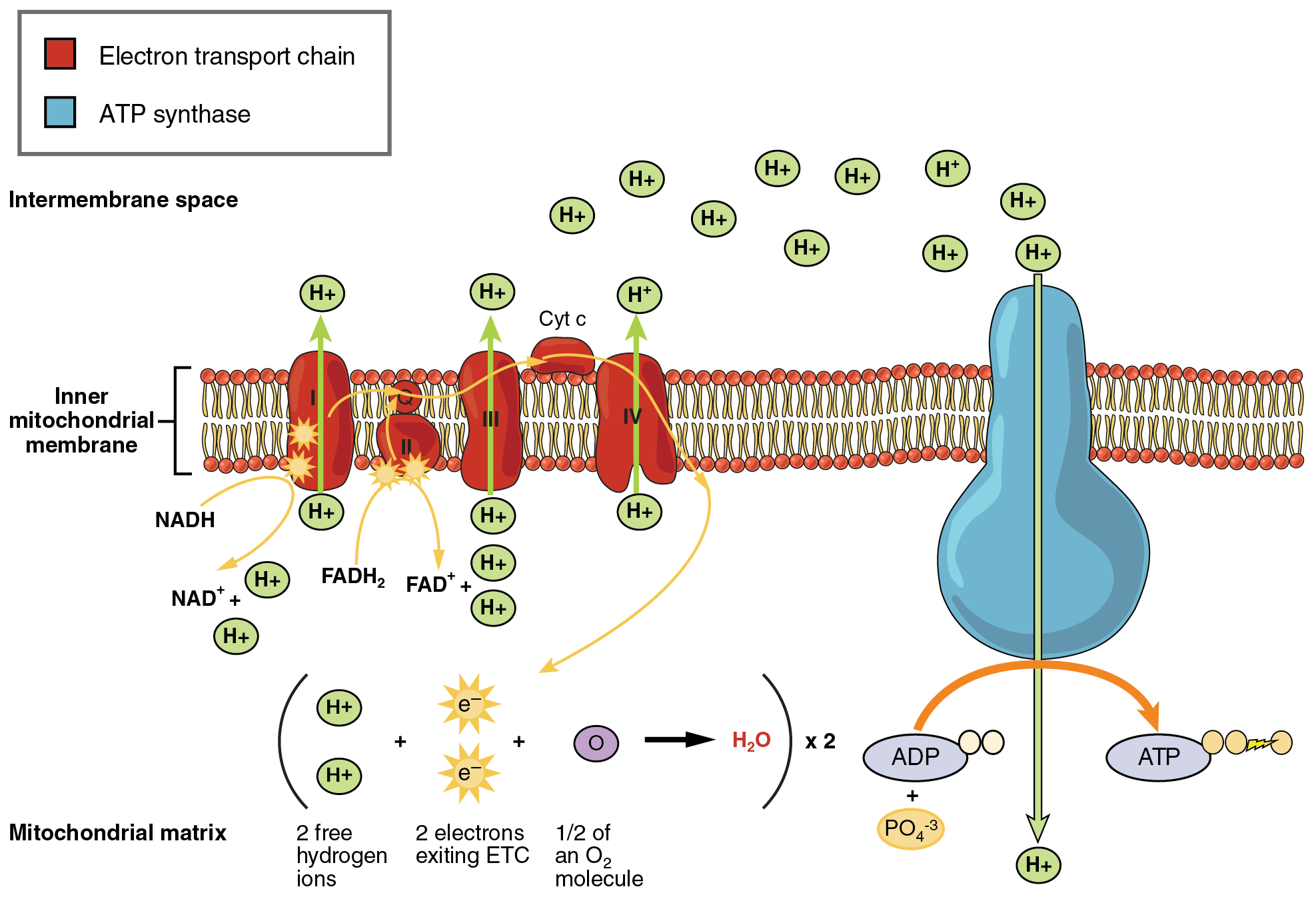
This process occurs in the mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell. Cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds in.