Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Signal transduction The transmission of signals from a cells outside to its inside. During cellular respiration glucose in the presence of oxygen is converted into carbon dioxide and water. But cellular respiration is slightly more complicated than just converting the energy from glucose into ATP.
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell. Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n.
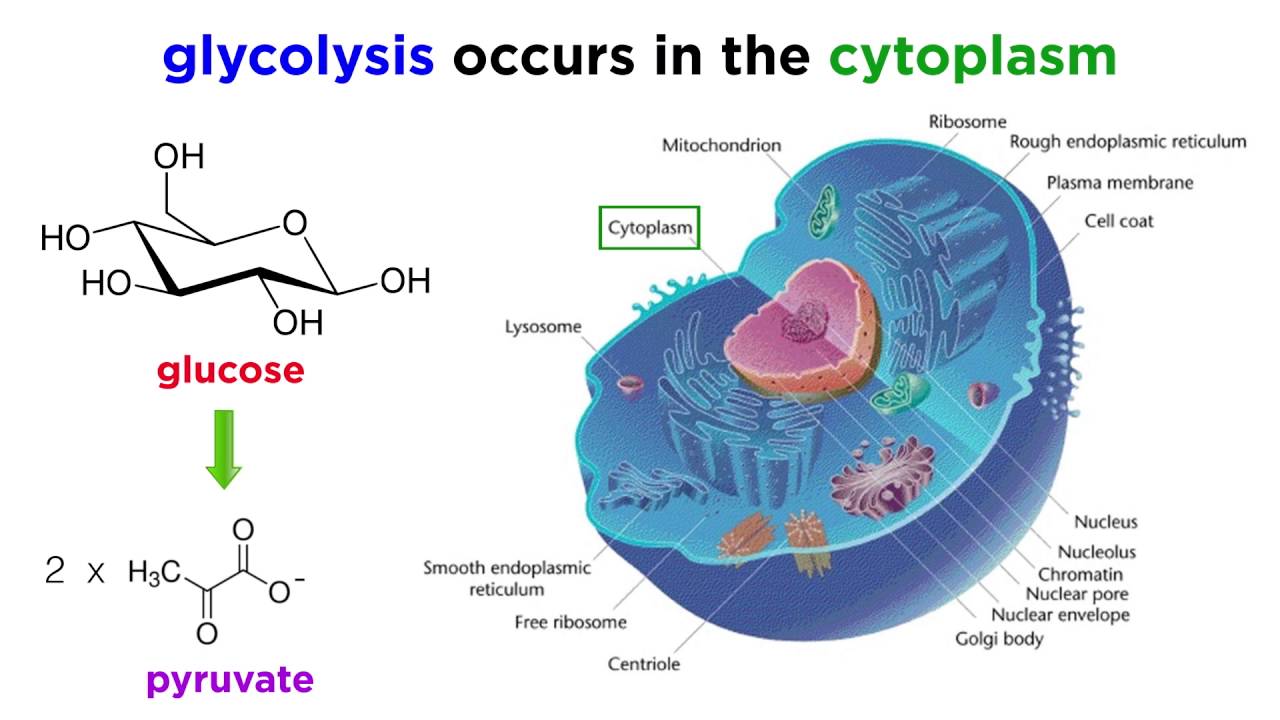
Other types of organisms such as animals fungi many protozoa and a large. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Cellular respiration stores chemical energy in the form of phosphorylated nucleotides primarily ATP by means of oxidative reactions and makes it available to other reactions.
Where cellular respiration happens. The respiration occurring at the cellular level wherein the cells produce energy by combining oxygen with food molecules is called cellular respiration. Introduction to Cellular Respiration.
The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells. Cellular respiration biology definition. Some organisms such as plants can trap the energy in sunlight through photosynthesis see Chapter 5 and store it in the chemical bonds of carbohydrate molecules.