Food Chain Definition Class 10

A food chain refers to the order of events in an ecosystem where one living organism eats another organism and later that organism is consumed by another larger organism.
Food chain definition class 10. Usually there are 3 or 4 trophic levels in the food chain. Food webs are helpful in explaining how disruptions in populations due to over- hunting poaching global warming and habitat destruction result in food scarcities leading to extinction Trophic level Definition. It may be because man occupies a position at or near the end of a chain of food items.
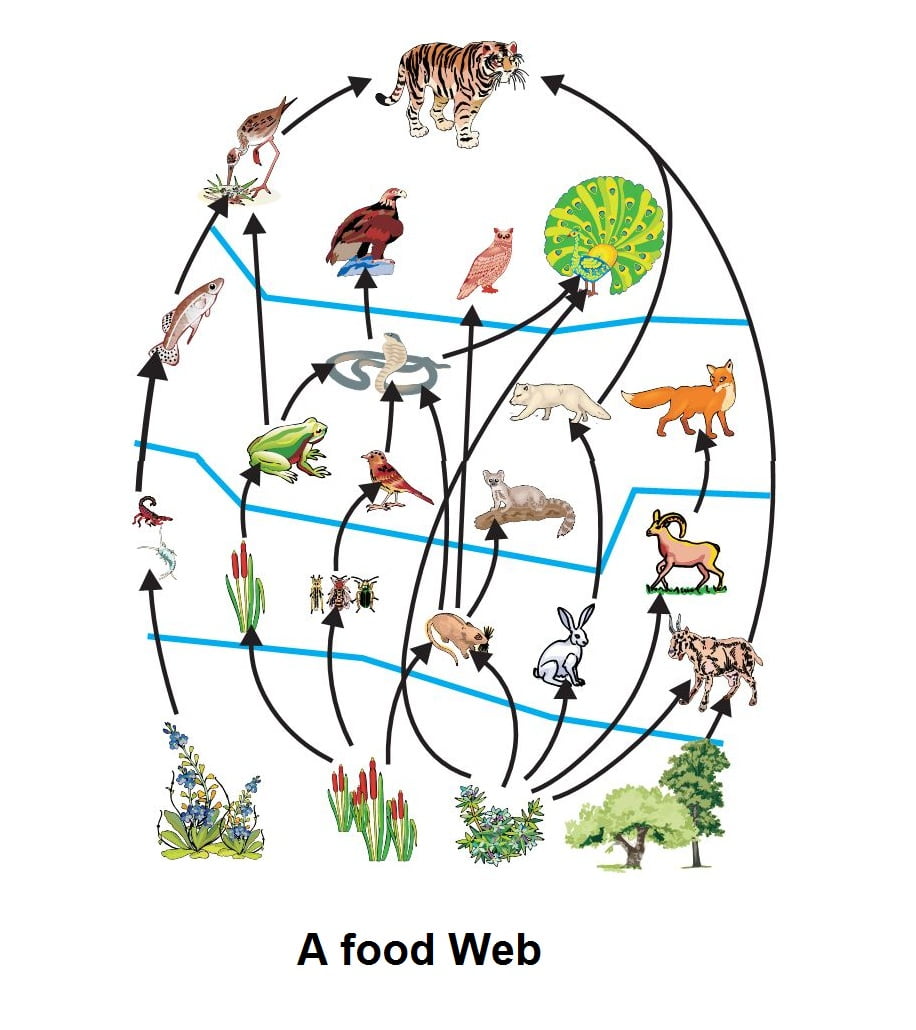
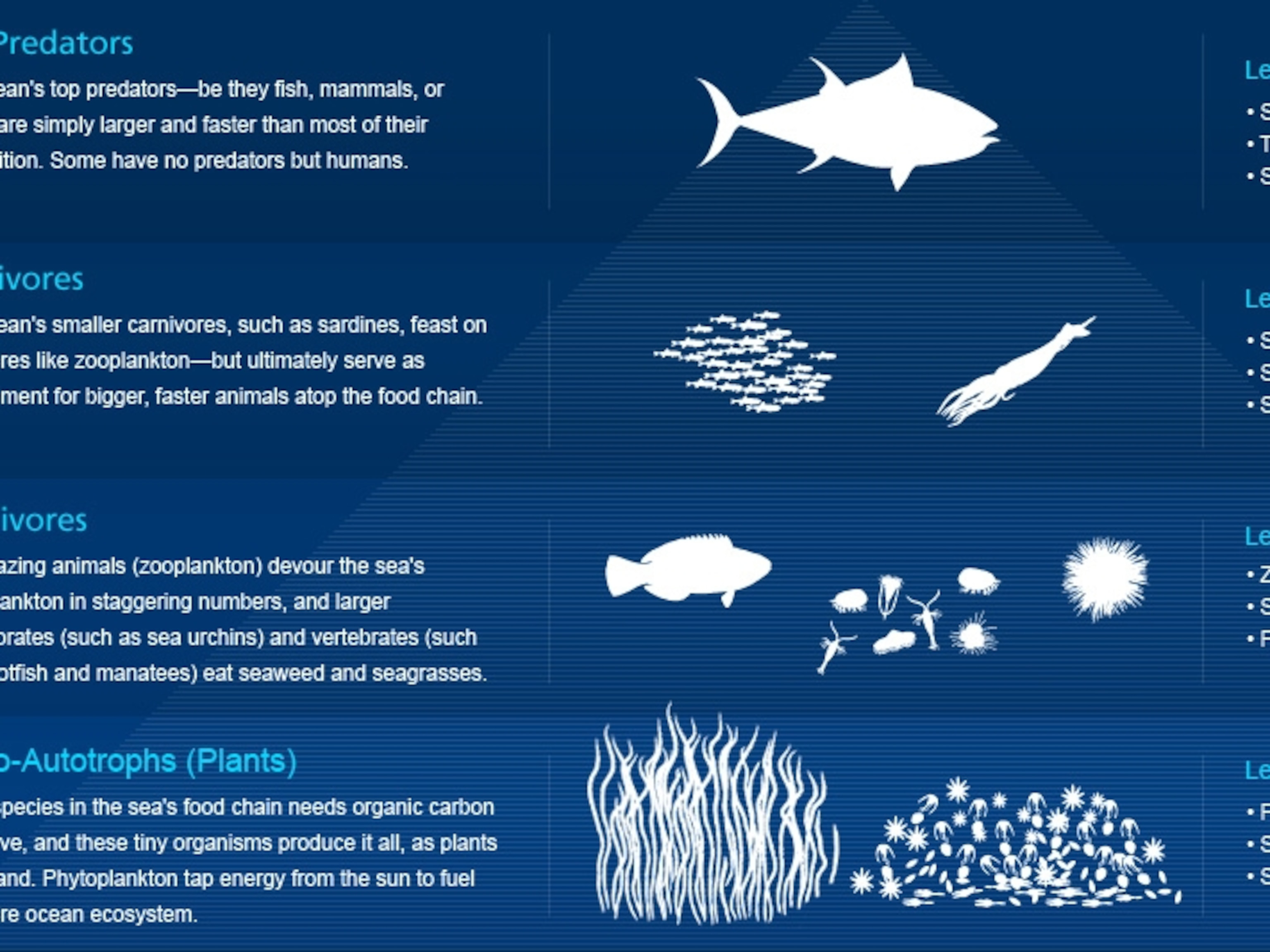
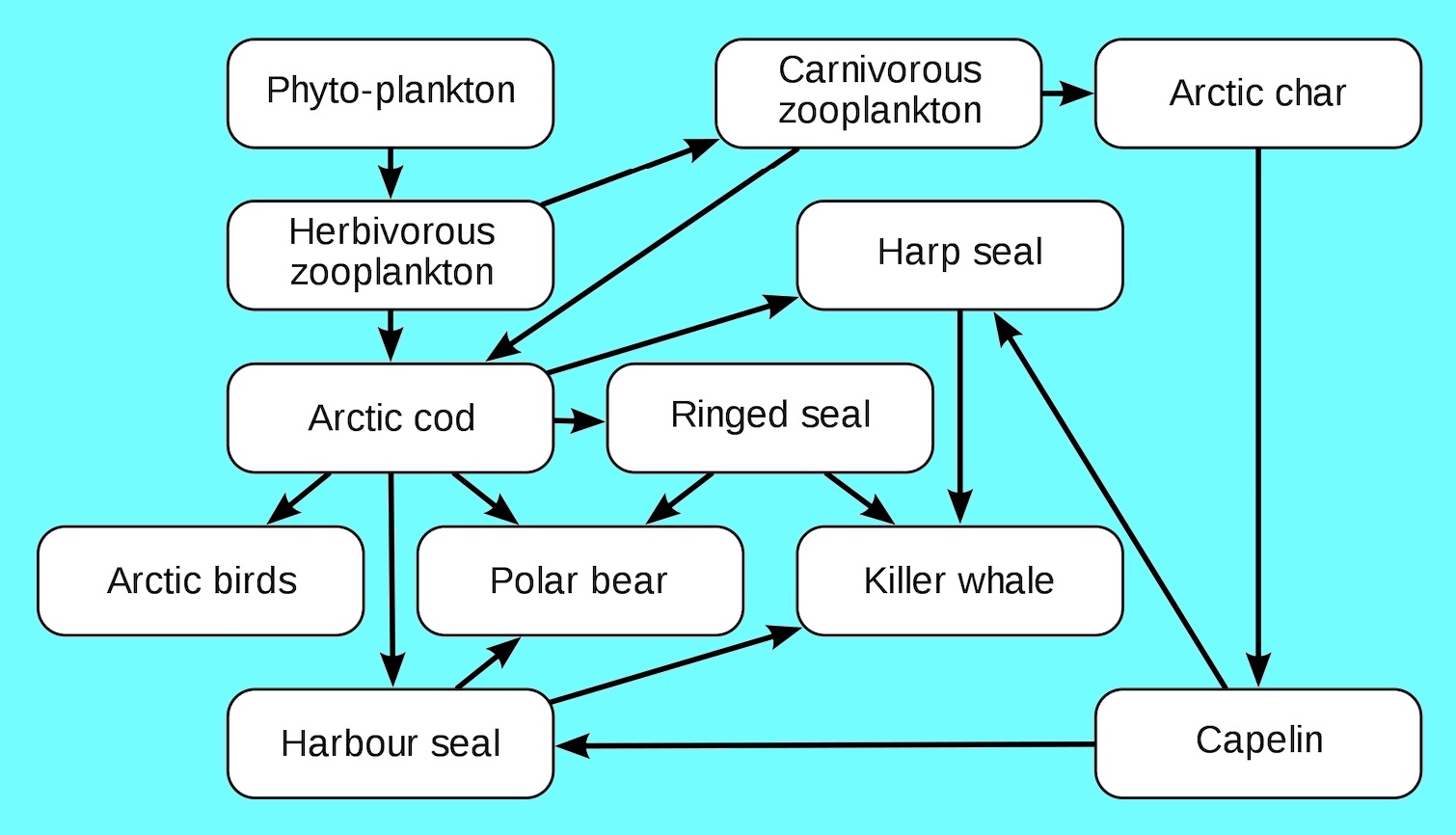
Any animal that is on top of the food chain is called an Apex. The flow of energy from one species to another at various biotic levels forms a food chain. Food Chain Food chain tells us how energy is transferred from one organism to another.
Although a food chain usually shows a line of animals that eat each other it is really a never-ending cycle that. This maintains a check on the population and a balance in the ecosystem. As a result a situation of eating and being eaten exists.
1 In all types of food chains one organism becomes the food of the other organism. A food chain usually consists of producers various. The gradual accumulation of harmful non biodegradable and chemical substances from one trophic level to next trophic level and then throughout The food chain is known as biological magnification.
A food chain describes how organisms get energy from eating other organisms. Kaneppeleqw and 459 more users found this. Each step in the food chain is a trophic levelLets took at this food chainSo in this food chainAt the bottom level we have theproducersThey generate food to be eatenExample - PlantsThe organisms that eat the producers are calledPrimary ConsumersThey are Herbivores plant.
The difference between an energy pyramid and a food chain is. Food chains are more or less familiar to everyone in a vague sort of way. Food chain is a sequence of organisms in a biotic community through which food passes with members of a step becoming food of the members of the next step of the sequence.