Food Chain Definition Ecology
This occurs when one organism consumes another organism.
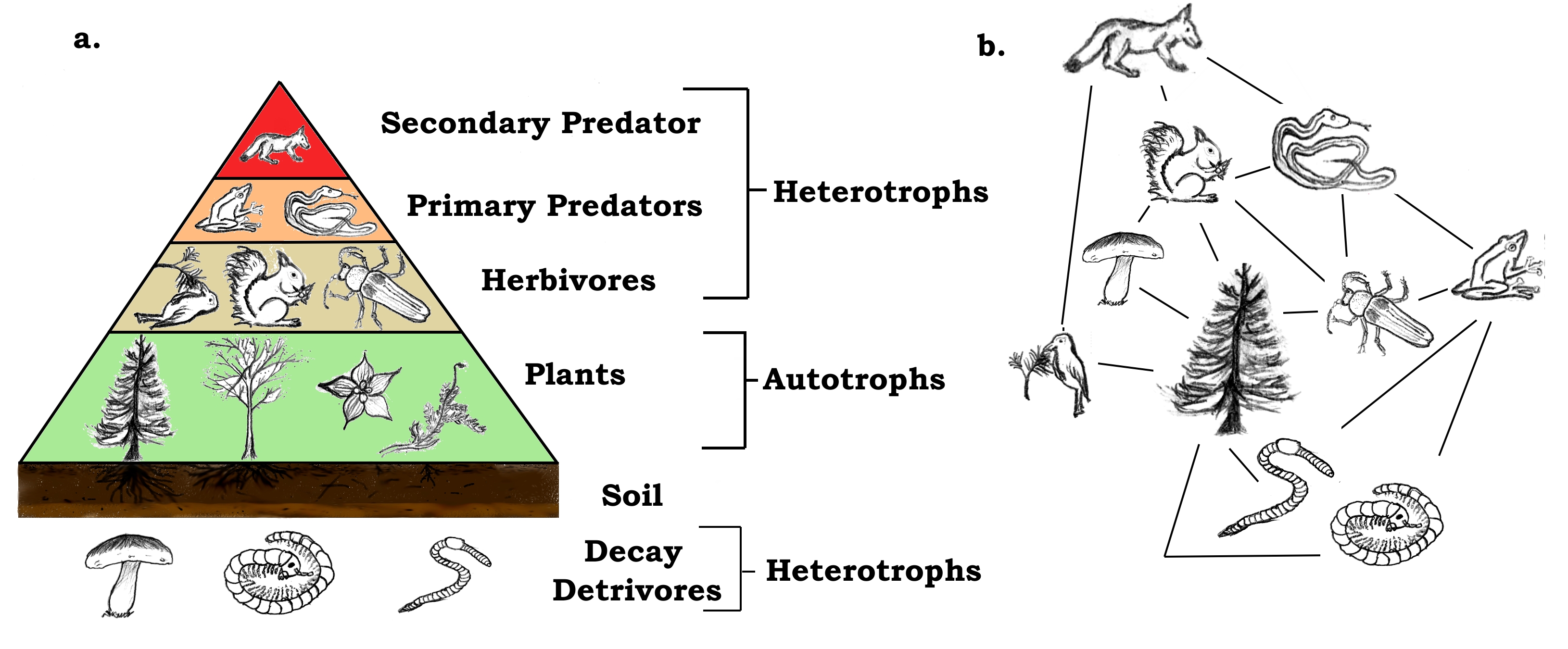
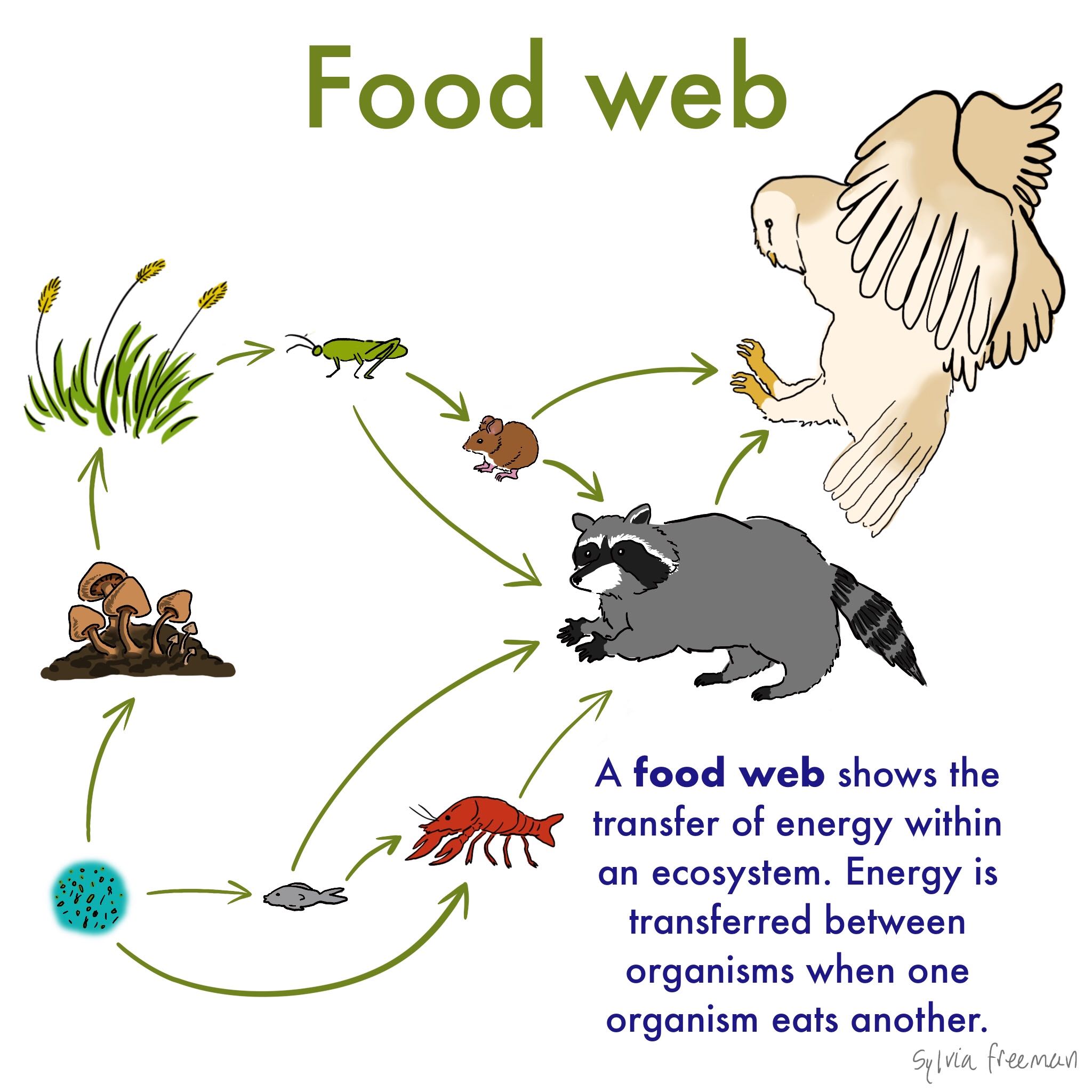
Food chain definition ecology. This cyclic transfer of food and the relation of food and its consumer are known as the food chain. Flow of energy in an ecosystem is one way process. The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild.
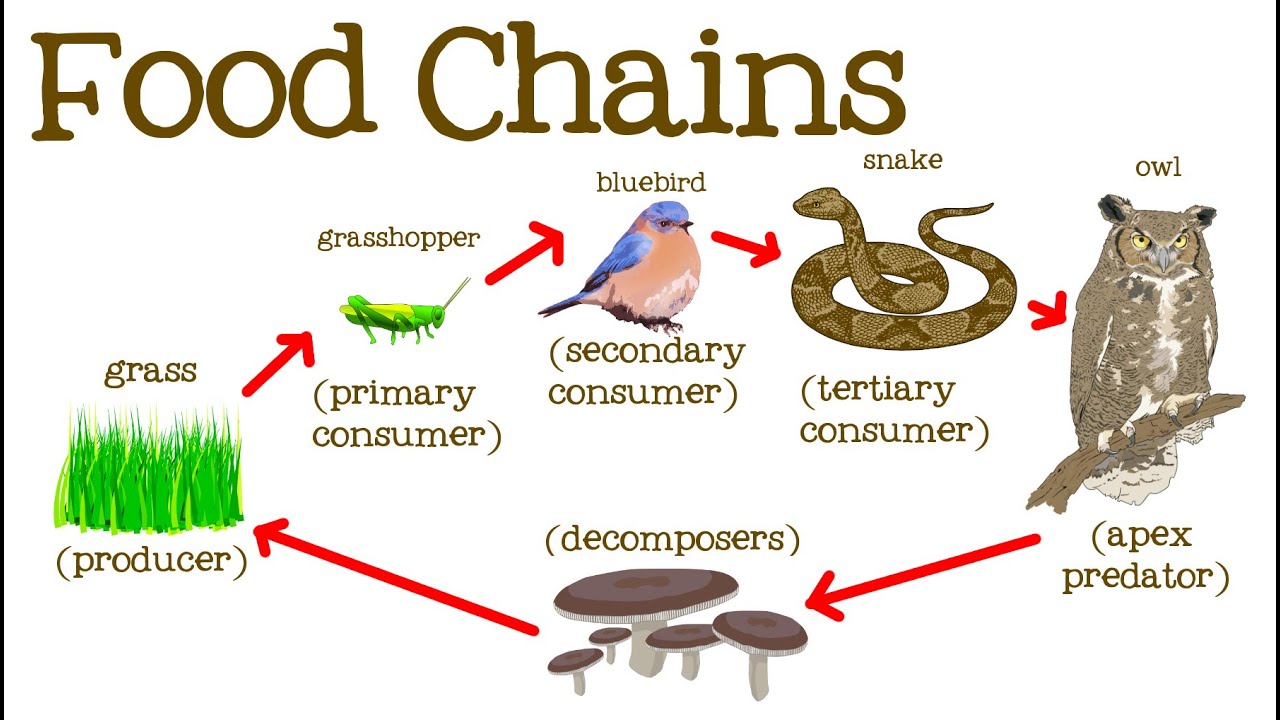
The food chain consists of four major parts. There are likely other naturalists between Linnaeus and Darwin who reported on food chains but attracted little notice. It shows the flow of energy and materials from one organism to the next beginning with a.
Find the Food Chain Definition Ecology including hundreds of ways to cook meals to eat. The consumers include all the other types of organisms in the. In 1927 he recognized that the length of these food chains was.
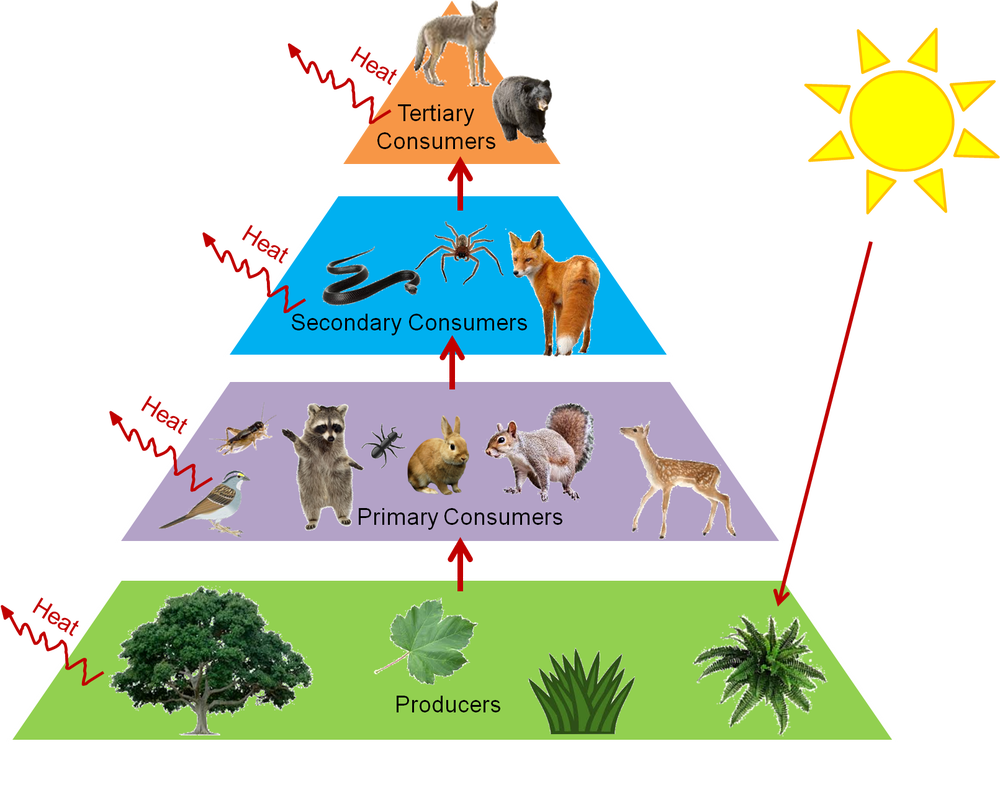
The food chain is an ideal representation of flow of energy in the ecosystem. Food chain definition ecology Thinking Food Chain Definition Ecology to Eat. In food chain the plants or producers are consumed by only the primary consumers primary consumers are fed by only the secondary consumers and so on.
English 1775114 1977 briefly itemized the stages of two food chains one terrestrial one aquatic Egerton 2007a. A food chain is basically made up of producers and consumers. A food chain shows what eats what in a particular habitat.
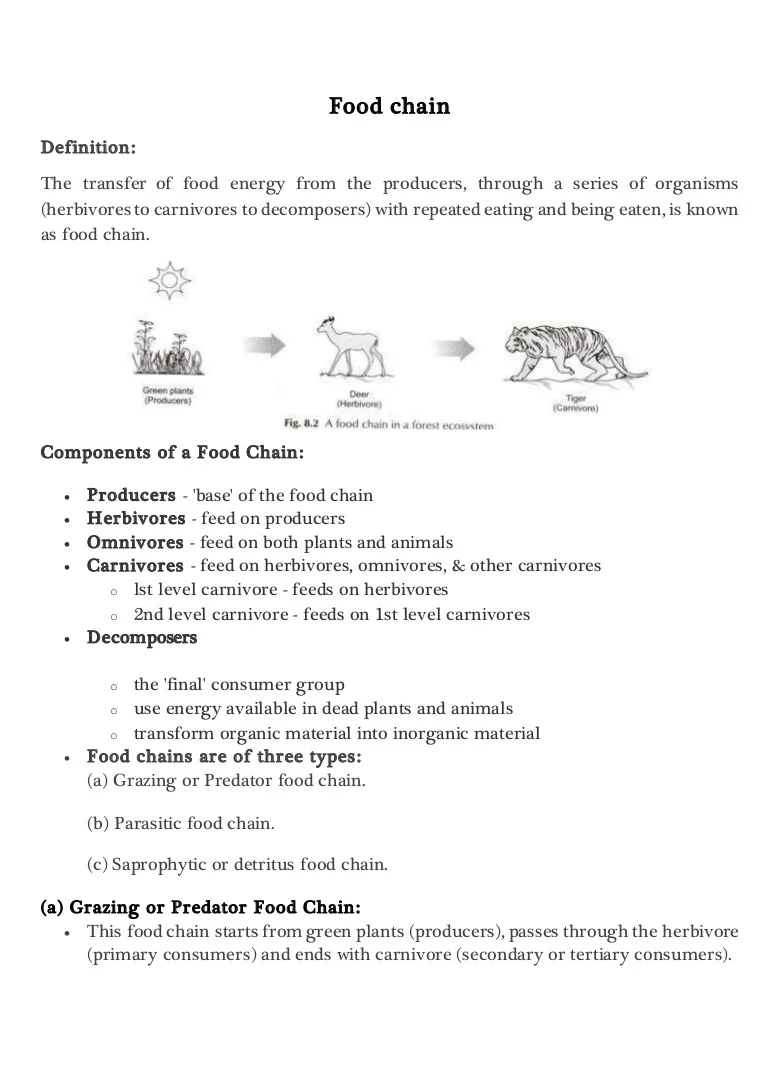
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the Sun to make their food and ending at an apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteriaA food chain also shows how organisms are. A food chain begins with a producer usually a green plant or alga that creates its own food through photosynthesis. The pattern of eating and being eaten forms a linear chain called food chain.