Transgenic Animals Applications And Examples

Use of transgenic animals will provide solutions for drug research xenotransplantation clinical trials and will prove to be a new insight in drug development.
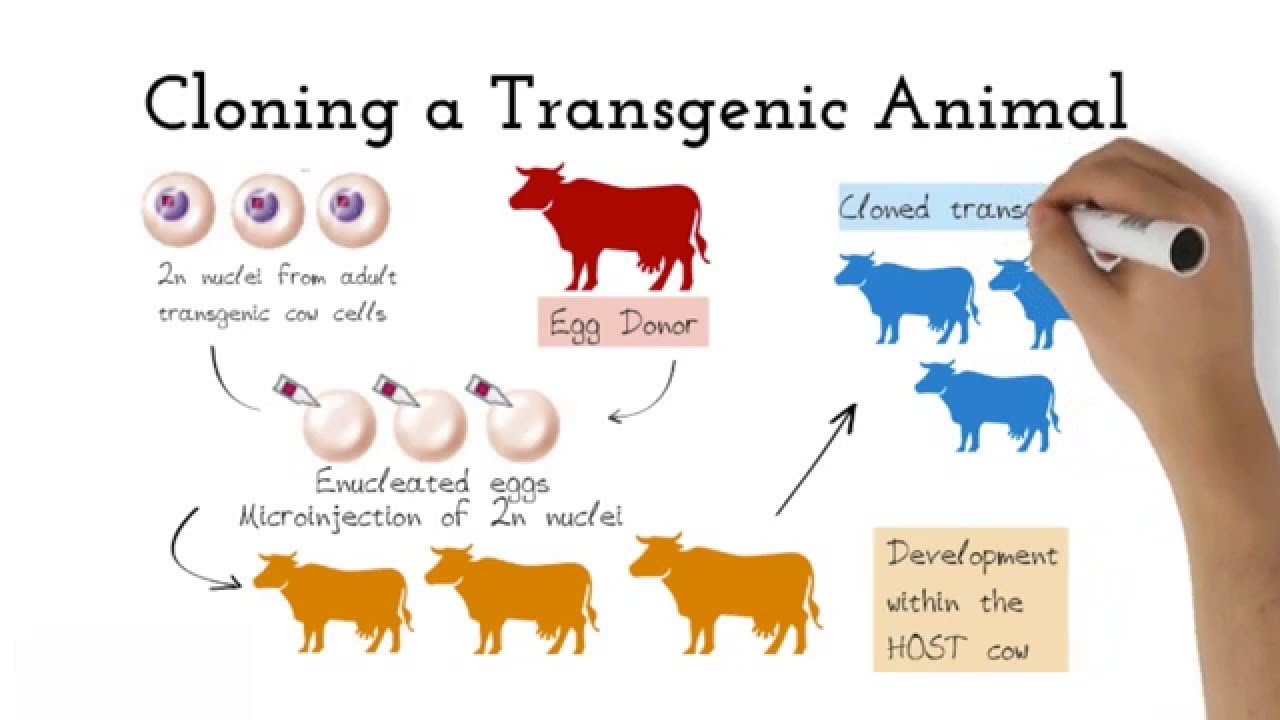
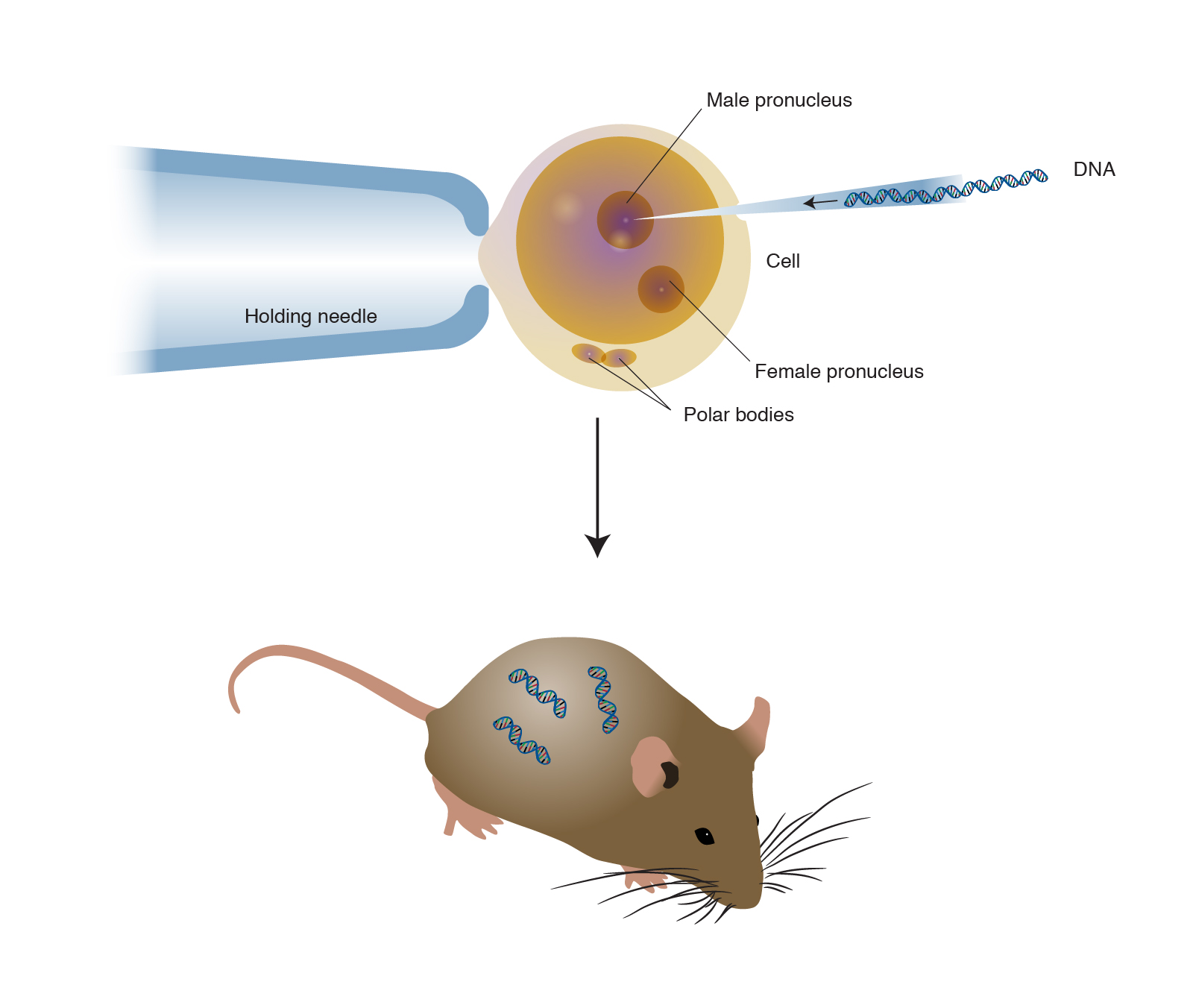
Transgenic animals applications and examples. When inserted successfully these genes enable an animal to produce for example pharmaceutical proteins in its milk urine blood sperm or eggs or to grow rejection-resistant organs for transplant. Telos is defined as the set of Drugs from Transgenic Animals in Clinical needs and interests which are genetically based Trials environmentally expressed and which collectively The approval of ATryn rATIII by USFDA has constitute or define the form of life or way of opened gates for other drugs from transgenic living exhibited by that animal and whose animals. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology.
One of them is the ability to engineer transgenic animals. 2 Some transgenic animals are used as models for detecting diagnosing and treating different diseases. Some important examples of transgenic animals are as follows.
Examples of transgenic organisms include mammals fish plants bacteria and viruses. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. Transgenic animals are animals that have been genetically transformed by splicing and inserting foreign animal or human genes into their chromosomes.
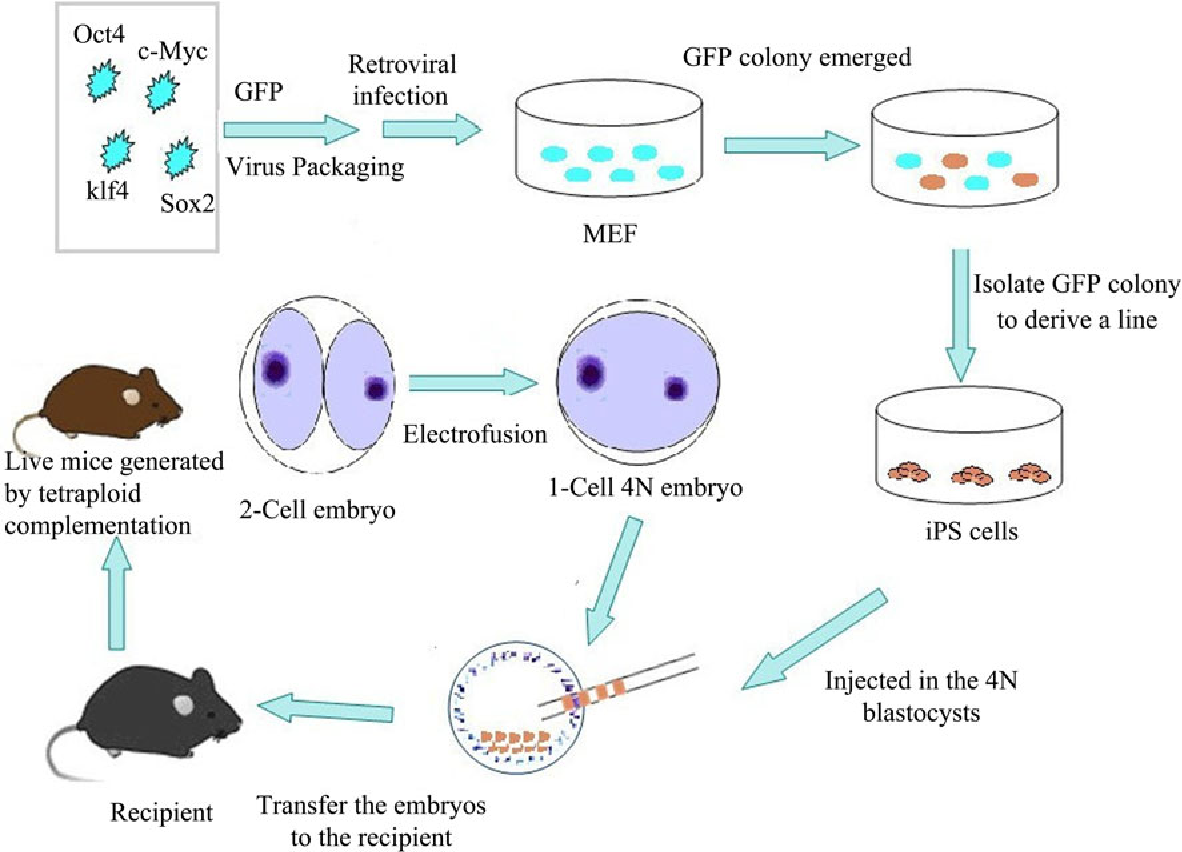
The first genetically modified organism was a bacteria created in 1973 by Stanley N. Tell the FDA NO Frankenfish. Pluripotent stem cell technology.
For example we have transgenic models for diseases such as Alzheimers and cancer. Scientists of Harvard produced a mouse carrying the genes which help in development of cancer. Transgenic animals ie engineered to carry genes from other species have the potential to improve human welfare.
Theoretically all living beings can be genetically manipulated. Transgenic Animals Applications And Examples. In addition to the gene itself the DNA usually includes other sequences to enable it to be incorporated into the DNA of the host and to be expressed correctly by the cells of the host.









_1602913203_391831-16.jpg)



_1602913203_391831-12.jpg)
