Transgenic Animals Definition Biology
Human transplant organ arising from an animal.
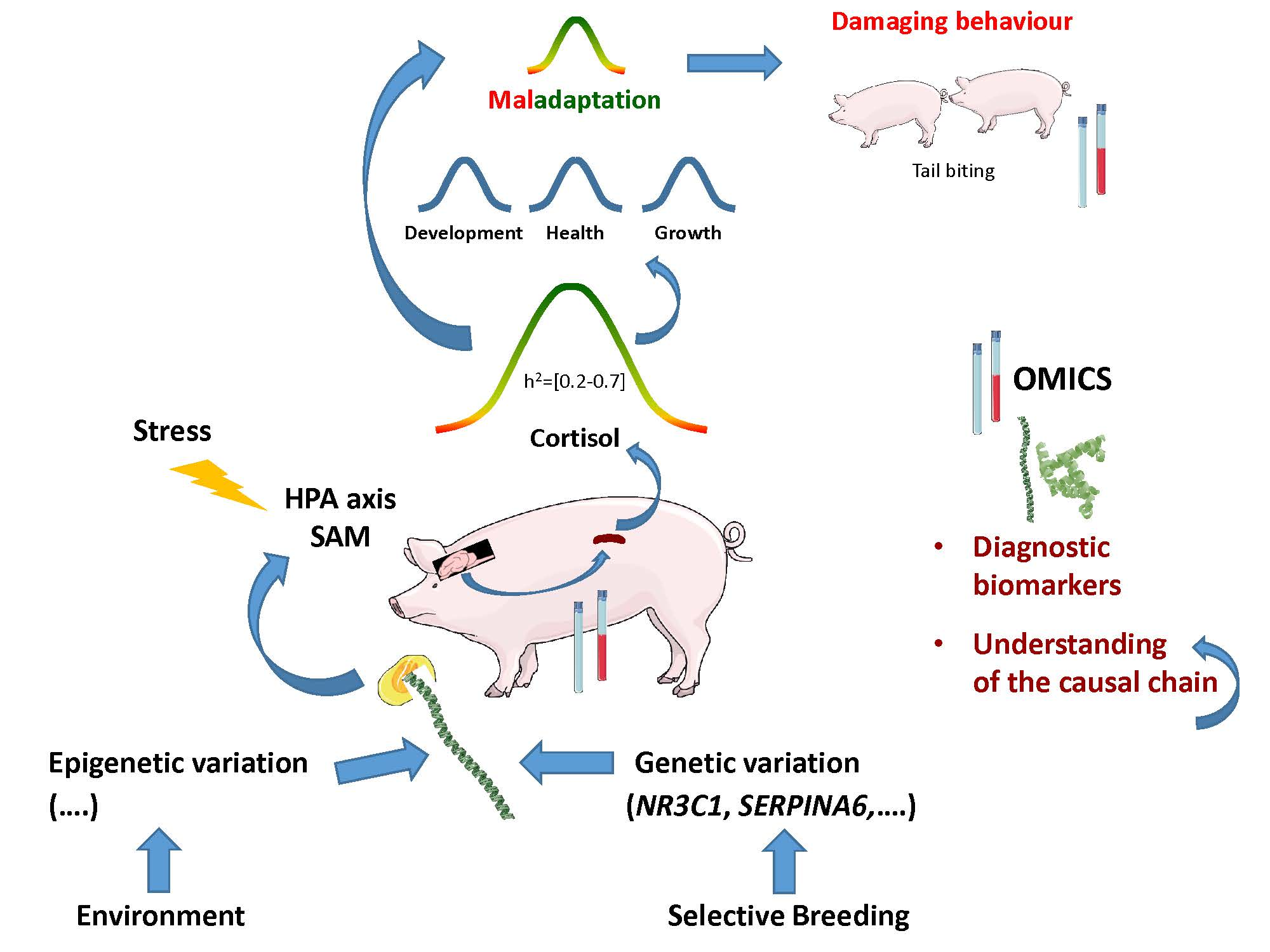
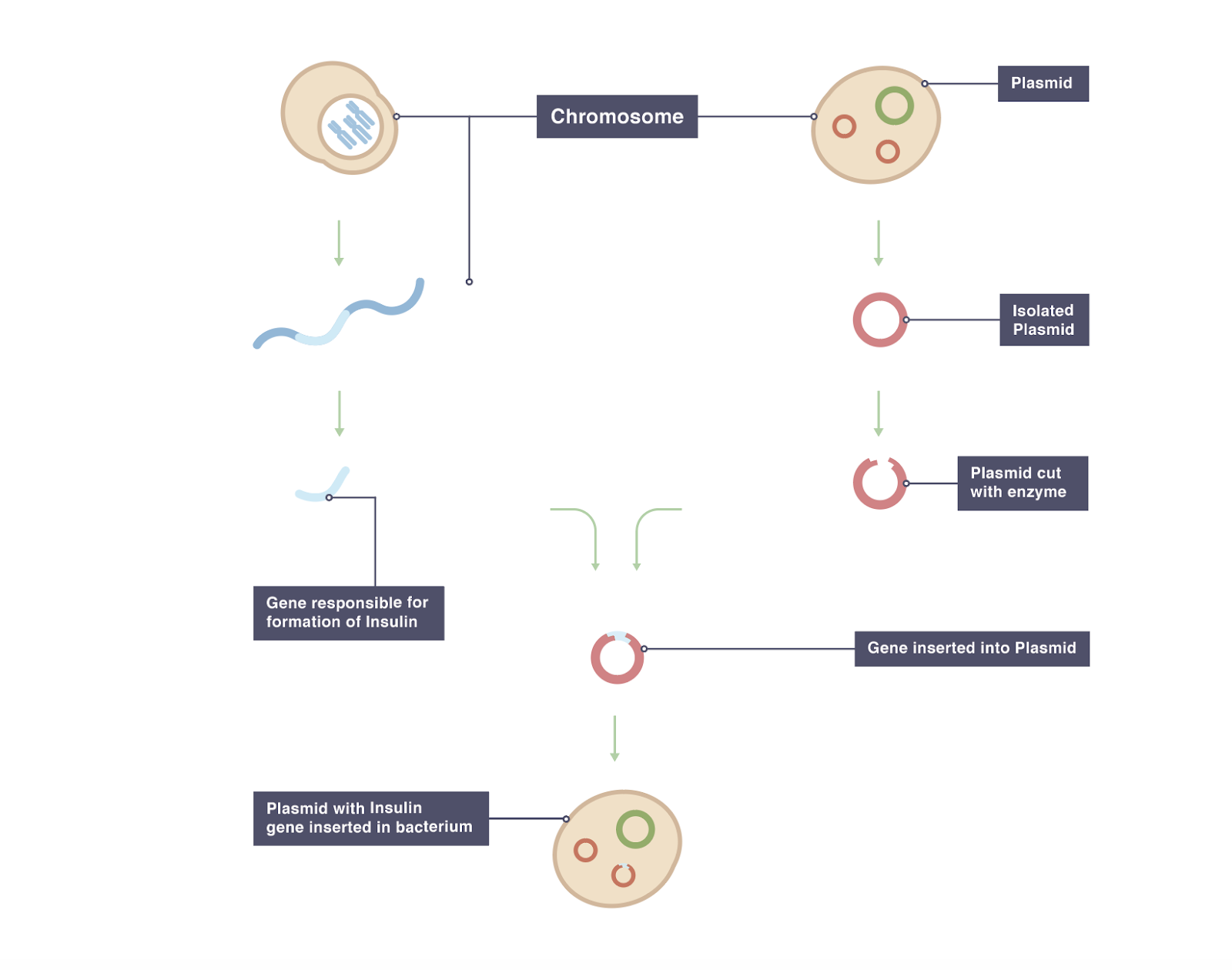
Transgenic animals definition biology. In addition to the gene itself the DNA usually includes other sequences to enable it. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. Transgenic animals are those that have been genetically modified.
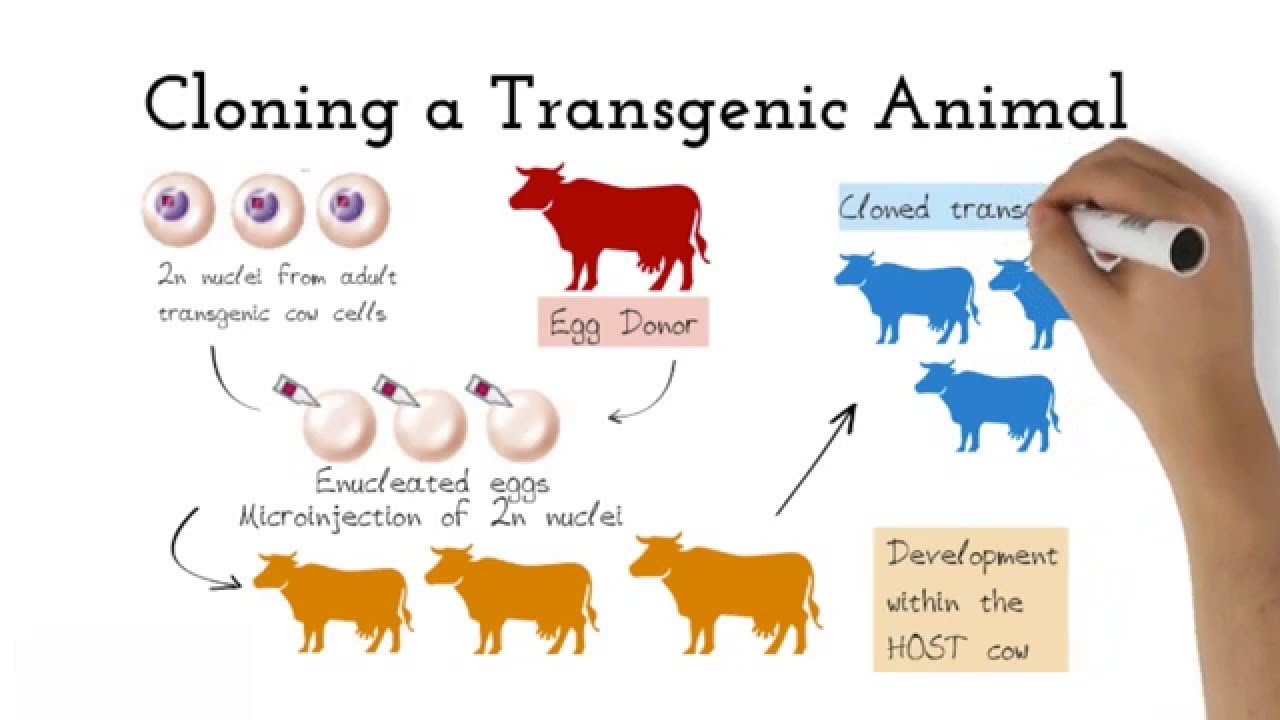
The foreign DNA or transgene that is transferred to the recipient can be from other individuals of the same species or even from unrelated species. Disease Animal Models - BSRC Alexander FlemingTransgenic Animal Models - Biomedcode. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology.
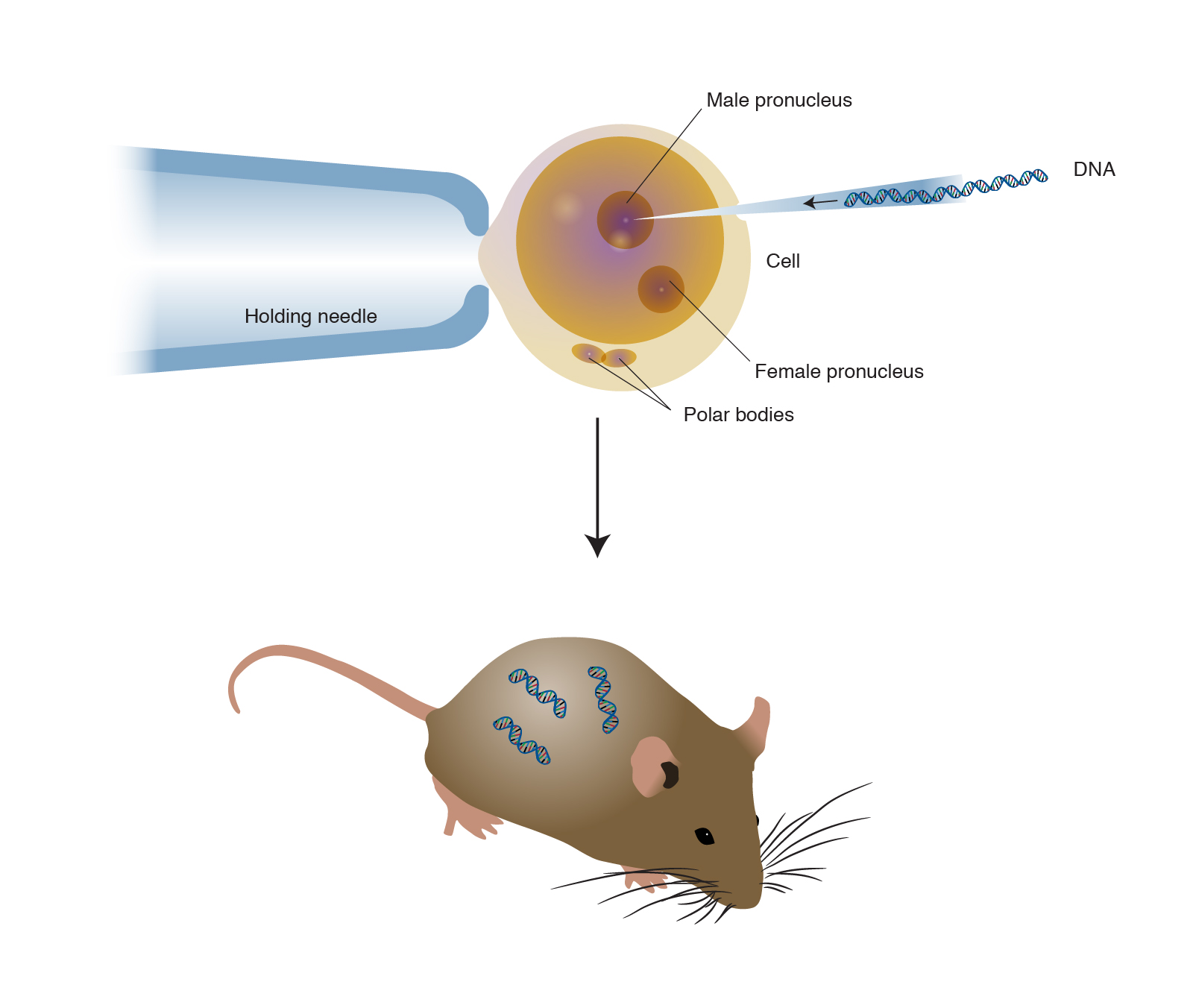
Full article A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been changed to carry genes from other species. Transgenic animals are specially designed to study the role of genes in the development of certain diseases. Animals transgenic animals or the offspring of such animals into which cloned genetic material has been experimentally transferred by microinjection of foreign dna either directly or into embryos or differentiated cell types.
Transgenic animals are also becoming useful commercially. BTransgenic animals are made that carry genes which make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals. In addition to the gene.
Moreover in order to devise a cure for these diseases the transgenic animals are used as model organisms. A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been altered by the transfer of a gene or genes from another species or breed. Foreign genes are inserted into the germ line of the animal so it can be transmitted to the progeny.
Transgenic Animals Definition Biology. Animals usually are made transgenic by having a small sequence of foreign DNA injected into a fertilized egg or developing embryo. The animal which carry foreign genes are called transgenic animals.

_1602913203_391831-5.jpg)